Nanocapsules Enable Cell-Inspired Metabolic Reactions
Researchers at the University of Basel succeeded in developing capsules capable of producing the bio-molecule glucose-6-phosphate that plays an important role in metabolic processes. The researchers were able to produce the metabolite in conditions very similar to the biochemical reaction inside natural cells. The results have been published in the scientific journal Chemical Communications.
19 September 2017
Metabolic processes inside living organisms involve a large variety of bio-molecules. These molecules are produced by specific enzymatic reactions. One example of such a bio-molecule is glucose-6-phosphate, a metabolite that is involved in important metabolic processes. It is central in the degradation of carbohydrates and can also be converted further into specific molecules responsible for storing energy within an organism. If such bio-molecules can be produced directly inside living cells, new perspectives in the treatment of disease would open up.
Nanocapsules produce glucose-6-phosphate
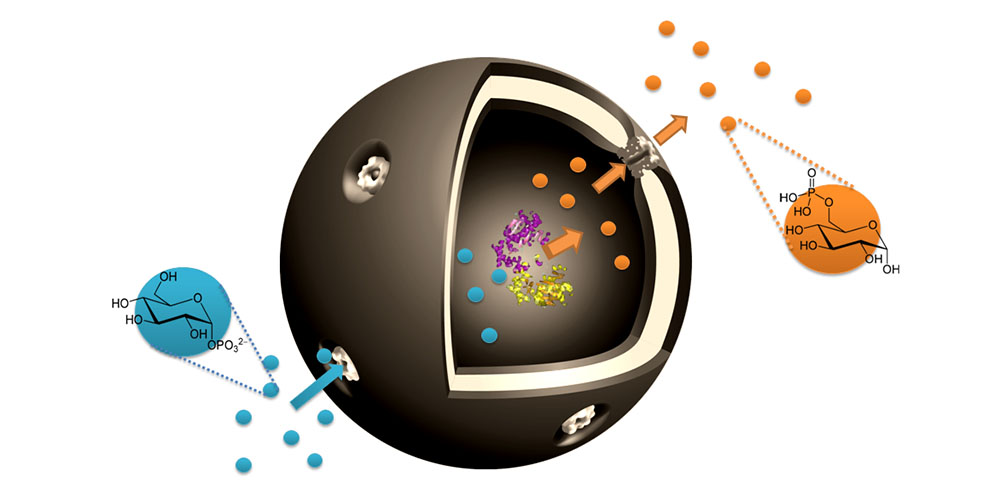
Researchers led by Prof. Cornelia Palivan from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Basel have designed bio-catalytic capsules that contain the active enzyme phosphoglucomutase and can produce and release glucose-6-phosphate.
To start the reaction, the substrate required for the reaction has to be able to enter the capsule. The researchers thus inserted a pore protein synthesized at ETH Zurich in the walls of the capsules. These pores are the entry door for the substrate and the exit for the product glucose-6-phosphate, while the enzyme remains encapsulated and protected against degradation.
The developed nanocapsules are less than 200 nanometers in size, which means they can be taken up by cells, an important prerequisite for future testing and application.
Unlike other approaches that use organic solvents, the researchers develop their capsules in conditions very similar to those in nature. “Our approach is always to be as nature-like as possible,” says Palivan “so we can preserve the intrinsic bio-functionality of the enzymes and pore proteins.”
In a next step, the researchers will now test the capsules on cells, to see if they are taken up and then produce glucose-6-phosphate inside the cell.
Original source
Mihai Lomora, Gesine Gunkel-Grabole, Shiksha Mantri and Cornelia G. Palivan
Bio-catalytic nanocompartments for in situ production of glucose-6-phosphate
Chemical Communications (2017), doi: 10.1039/C7CC04739H