NCCR QSIT
Together with ETH Zurich, the Department of Physics at the University of Basel leads the National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) for the development of novel quantum systems.
The NCCR QSIT – Quantum Science and Technology is a collaborative platform for creating the basis, tools and methods to translate fundamental advances in quantum science into fundamentally new technological capabilities.
One of the outstanding achievements in physics in recent decades was the increasing ability to control individual quantum particles such as photons or atoms. This paved the path to entirely new ways of thinking about future technologies. Lasers, solar cells and the semiconductor materials that make modern electronics possible – these and other established technologies rely implicitly on quantum mechanical effects. By contrast, quantum effects take centre stage in «quantum technologies». The latter are engineered around systems whose quantum properties can be tuned, controlled and exploited in applications, from sensors with unprecedented sensitivity and precision to potentially disruptive technologies for processing, transferring and storing information.
The leap from using the quantum behaviour of existing materials to designing, building and exploring novel quantum systems requires new levels of theoretical understanding, experimental capabilities and engineering proficiency. Such an endeavour can be accomplished only in a concerted effort across disciplines. In Switzerland, the NCCR «QSIT» is the driving force behind such efforts.
Aims and achievements
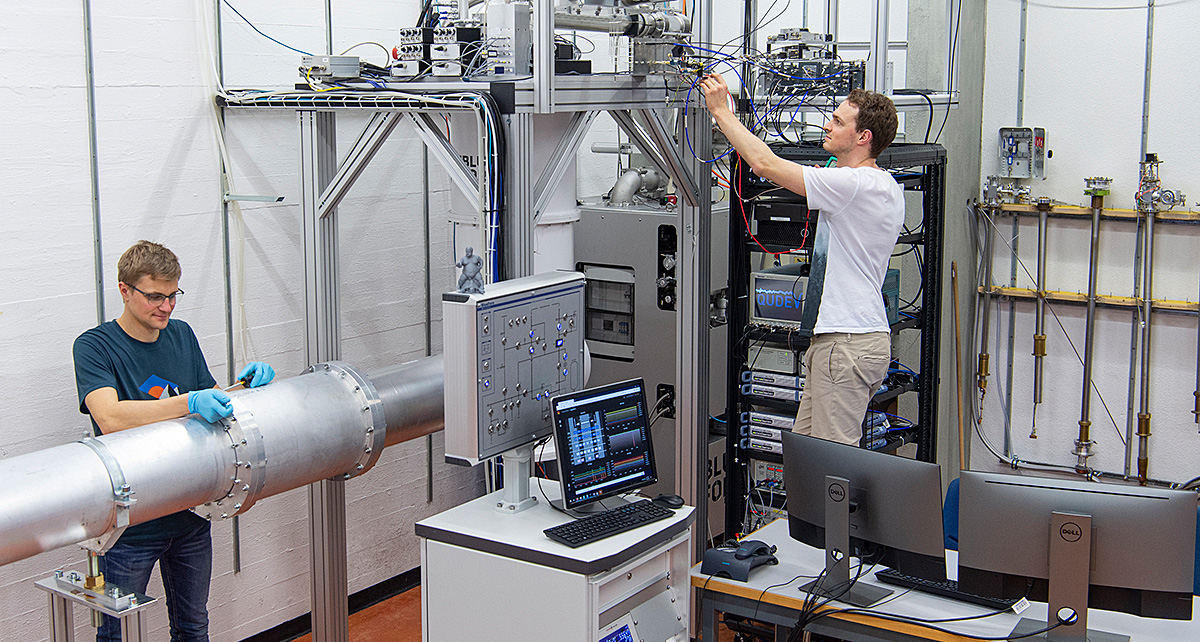
In order to develop quantum systems for new scientific and technological applications, the NCCR «QSIT» combines concepts from physics, chemistry, engineering and computer science. On the one hand, systems are created in which quantum states with tailored properties can be realized. For this purpose, high-purity and precisely structured materials are fabricated, from one-dimensional nanowires and ion chains to two-dimensional electron systems and superconducting circuits, to nano- and micromechanical oscillators as well as atomic gases in optical lattices. A specific strength of the QSIT network are hybrid devices that combine different types of quantum systems developed by separate groups.
On the other hand, these quantum systems are used in various ways. For example, they can interact with their environment in a manner that is fundamentally different from the behaviour of classic systems. This is the basis for novel sensors that are superior to conventional systems in terms of sensitivity and precision, pushing both to the fundamental limits. These advantages can be used to measure physical quantities such as magnetic and electrical fields, time and frequency, force and displacement or temperature. For exploiting this potential fully in ultra-sensitive devices, fundamental theories for quantum measurements have be developed alongside novel quantum hardware.
This interplay between theory and experiment also characterizes research in the field of quantum computing and quantum communication. Quantum computers have the potential to solve open problems in quantum physics, material design and chemistry that even the most powerful conventional computers cannot crack, while quantum communication enables the transmission of information with unprecedented security against eavesdropping. Researchers at NCCR «QSIT» are paving the way to these goals by developing quantum systems that will serve as building blocks for such future technologies.
Similar methods and systems are also used in so-called quantum simulators. There, a quantum system that can be precisely controlled and manipulated is used to emulate the behaviour of another quantum system, whose properties and behaviour cannot be studied directly. This approach enables unique insight into materials, engineered systems and theoretical models.
Beyond this diverse research agenda, the NCCR «QSIT» sees itself also as a catalyst for the creation of a new community. As one of the earliest initiatives worldwide dedicated to exploring future quantum technologies, the network has been pursuing since 2011 a broad educational programme to train future generations of quantum researchers as well as various technology transfer activities, to help bringing intellectual and technological advances to the marketplace, and ultimately to society.
As the field gradually matured during the lifetime of NCCR «QSIT», its members were also instrumental in initiating further innovative initiatives, including the Masters in Quantum Engineering at ETH Zurich and the NCCR «SPIN», led by the University of Basel and IBM Research Zurich.
Interdisciplinary network
NCCR «QSIT» brings together essentially all major players in the field of quantum science and technology in Switzerland. Currently more than 30 research groups are members, from ETH Zurich, the University of Basel, the University of Geneva, IBM Research Zurich, EPF Lausanne, USI Lugano and the University of Bern.
NCCR «QSIT» facilitates strong interactions between members and helps to overcome boundaries between different approaches. In this manner central strengths of the network, complementarity and breadth, can be leveraged to create fresh ideas and collaborations – and thus ever new opportunities in an ever-more vibrant field.
The Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) supported the NCCR «QSIT» in the first and second funding period (2011–2018) with CHF 37 million, and in the third funding period (2019–2022) with another CHF 15 million.