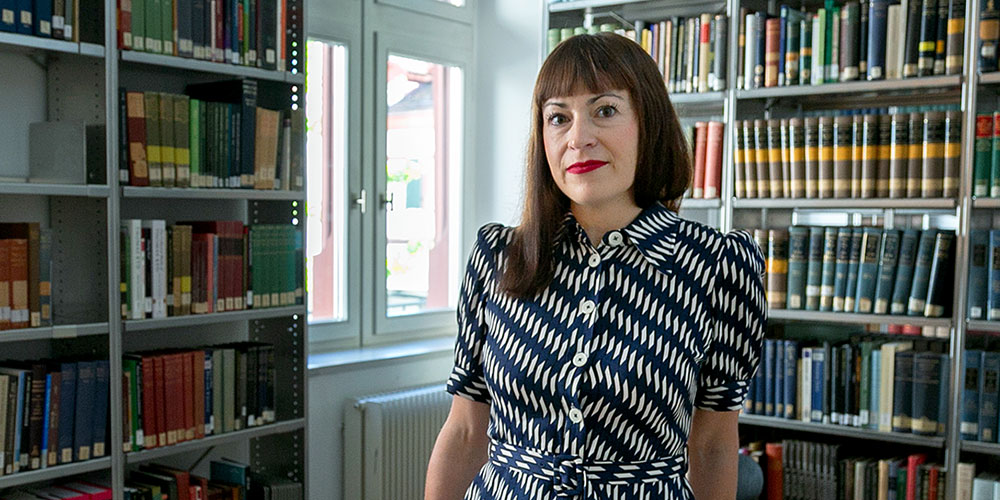
Why are more and more people in Western democracies yearning for destruction? And why do they vote for parties that promise just that? Literary sociologist Carolin Amlinger unpacks the roots of the global rightward shift and reveals why even Switzerland isn’t immune.

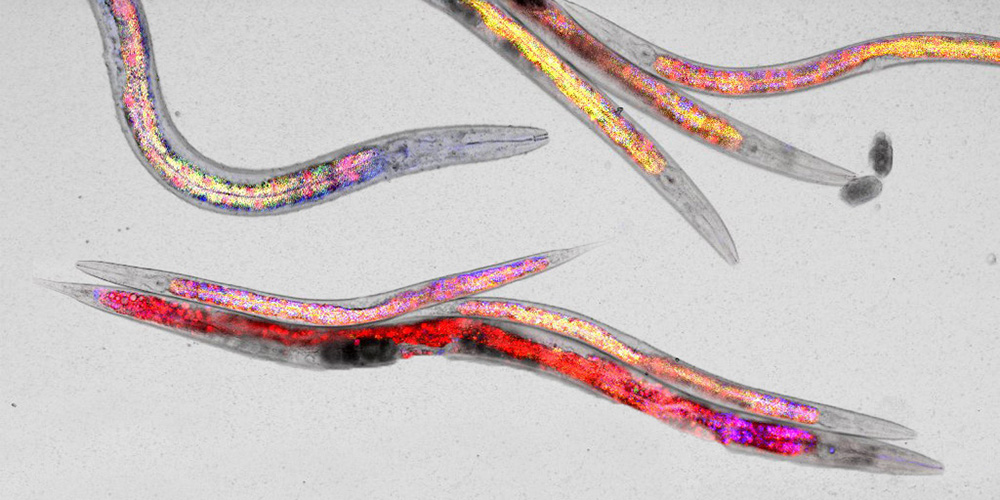
Certain nutrients in food can trigger a mild stress response in nematodes. But instead of making them sick, this actually helps them stay healthier as they age, according to researchers at the University of Basel.
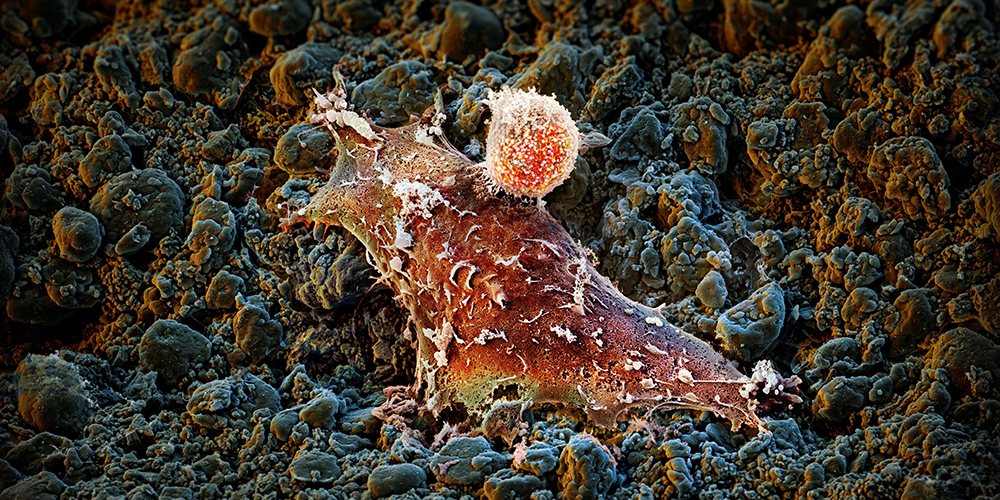
A newly developed molecule brings together two powerful immunotherapy strategies in one treatment. Researchers at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel have demonstrated that this fusion protein can both block the “do not attack” signal used by cancer cells and selectively activate tumor-fighting immune cells. This dual action could pave the way for more effective cancer therapies with fewer side effects.
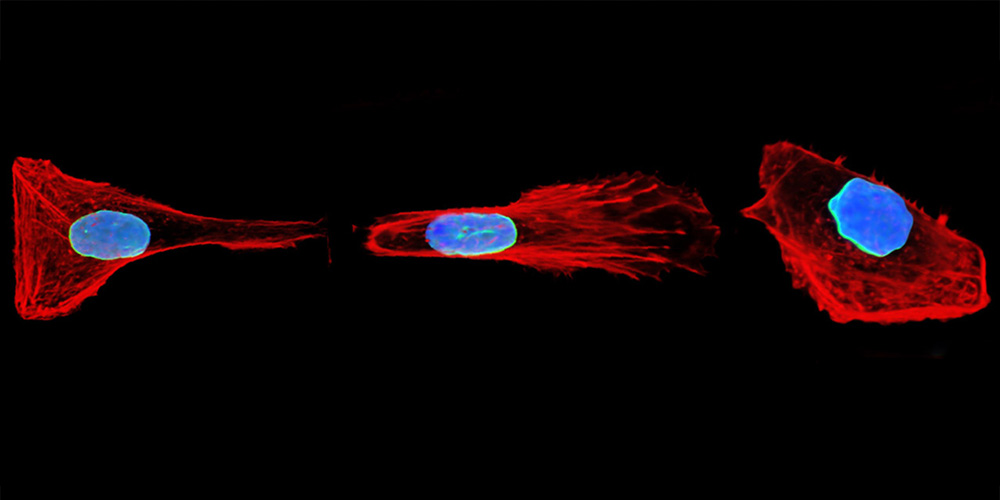
In wound healing, immune response, and cancer metastasis, cells migrate through the body – often squeezing through narrow, confined spaces. Together with experimental collaborators, Prof. Dr. David Brückner at the University of Basel has discovered that cells possess a kind of memory: they can “remember” how they previously navigated such constrictions. This allows them to move more quickly and efficiently through complex tissues.
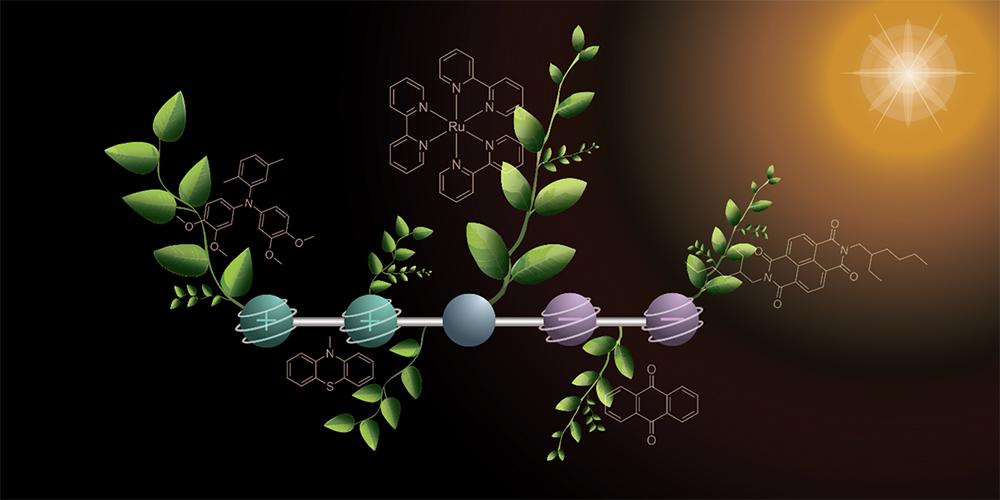
A research team from the University of Basel has developed a new molecule modeled on plant photosynthesis: under the influence of light, it stores two positive and two negative charges at the same time. The aim is to convert sunlight into carbon-neutral fuels.
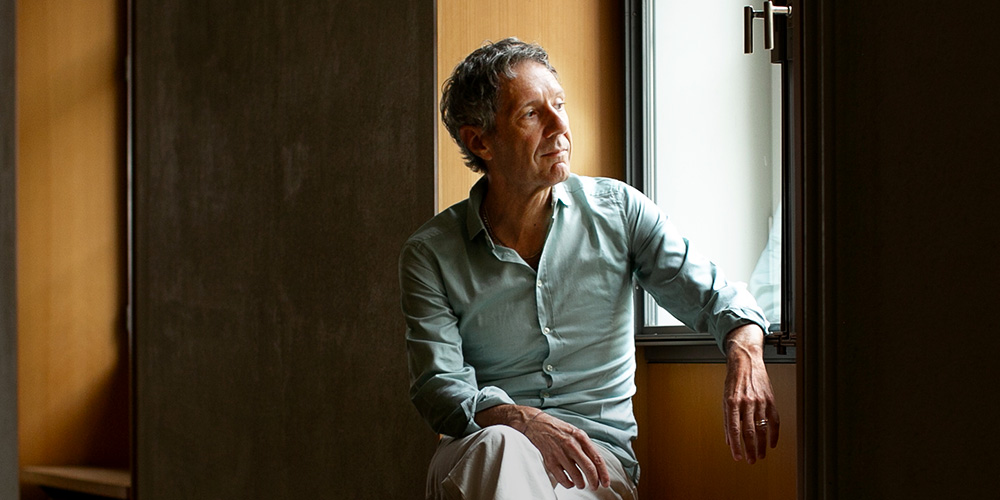
August 25 marks the 125th anniversary of the death of philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche, who was professor at the University of Basel from 1869 to 1879. In this interview, literary scholar Professor Hubert Thüring discusses the relevance of Nietzsche's writings and their continued importance today.

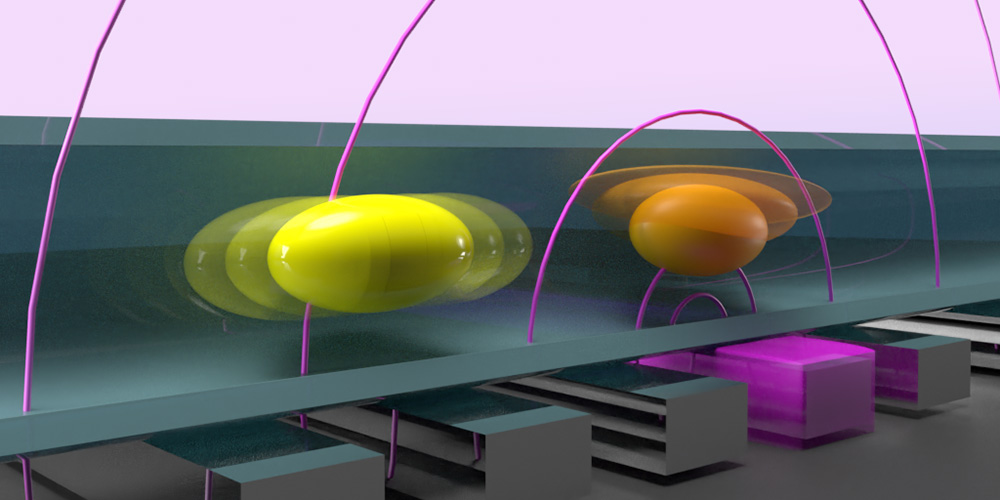
Researchers at the University of Basel have made a quantum bit faster and more robust at the same time. In the future, this could help in the development of quantum computers.
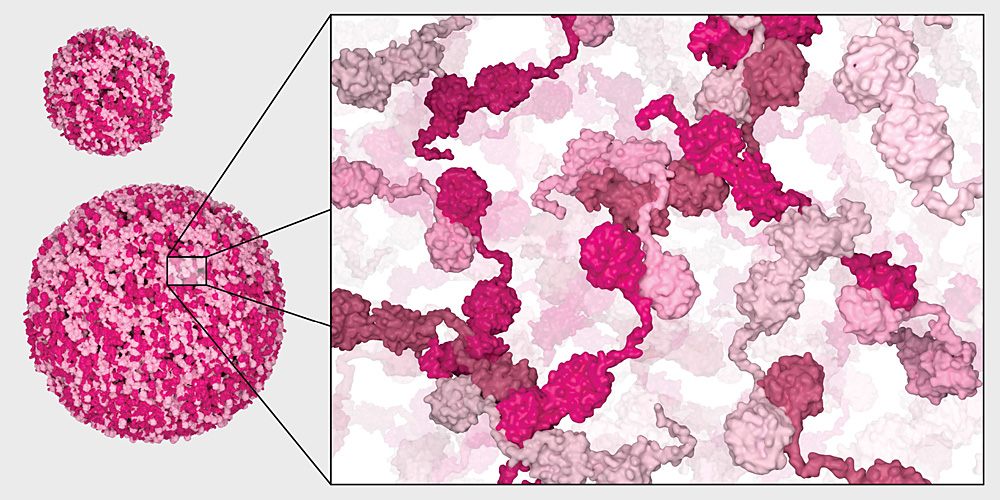
In order to fulfil their many functions, proteins must be folded into the correct shape. Researchers at the University of Basel have now discovered tiny “folding factories” in cells that enable efficient and accurate protein folding. A lack of these structures can lead to diseases such as diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders.
Korean TV dramas resonate with global audiences. This is thanks in no small part to a dedicated community that translates K-dramas, provides commentary, and supplements them with cultural explanations. Researchers at the University of Basel have investigated how meaning is collectively negotiated and how individual streaming is transformed into a communal experience.