Students of the English department present their research results in the form of a podcast. In eleven contributions they explore the cultural reasons for “Brexit” as well as the reactions to the decision of Britons to leave the European Union. The podcast in English is now available online.

The young startup of the University of Basel, Qnami, is the winner of the Venture Kick prize worth 130’000 Swiss Francs. Qnami develops precise and highly sensitive quantum sensors that provide images in nanometer resolution.

Fats are essential for our body. The core components of all fats are fatty acids. Their production is initiated by the enzyme ACC. Researchers at the University of Basel’s Biozentrum have now demonstrated how ACC assembles into distinct filaments. As the researchers report in “Nature,” the type of filament formed controls the activity of the enzyme and thus fatty acid production.
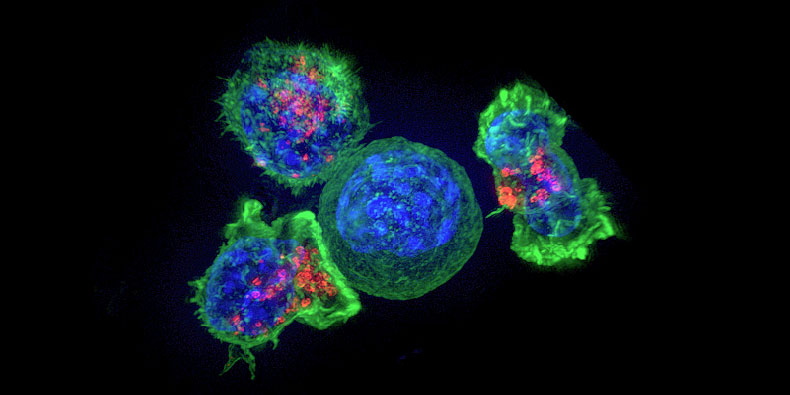
Doctors are increasingly fighting cancer by stimulating patients’ immune systems. Researchers have now discovered a method for predicting the likelihood of treatment success, as reported by researchers from the University and the University Hospital Basel in the journal Nature Medicine.
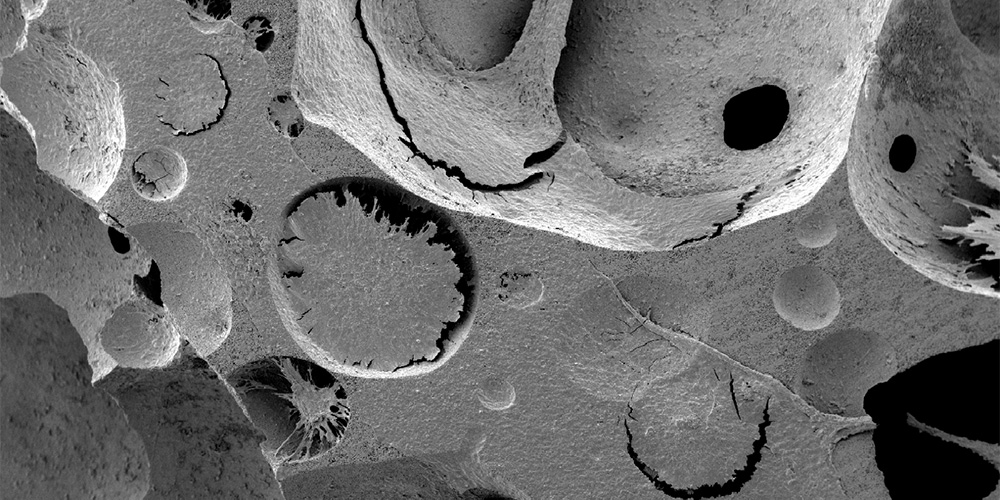
Researchers have developed an artificial tissue in which human blood stem cells remain functional for a prolonged period of time. Scientists from the University of Basel, University Hospital Basel, and ETH Zurich have reported their findings in the scientific journal PNAS.
The way in which the phase-out of nuclear power plants in Germany is currently planned could negatively influence the safety of the facilities. Those involved could increasingly favor their own interests as the shutdown date approaches.

Water molecules exist in two different forms with almost identical physical properties. For the first time, researchers have succeeded in separating the two forms to show that they can exhibit different chemical reactivities. These results were reported by researchers from the University of Basel and their colleagues in Hamburg in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Atsushi Shibasaki is researching cultures and cultural exchange as a visiting professor at the University of Basel’s Institute for European Global Studies. He talks about the friendliness of Basel’s inhabitants, parallels between Japan and Switzerland, and the importance of Bob Dylan.

The Senate of the University of Basel yesterday elected Torsten Schwede as its new Vice President for Research. Schwede is currently professor of bioinformatics at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel and a member of the Executive Board of Directors at the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB).